We discuss the importance of signal integrity, review high-speed deployment challenges, and highlight various connector design strategies to prevent distortion and degradation.
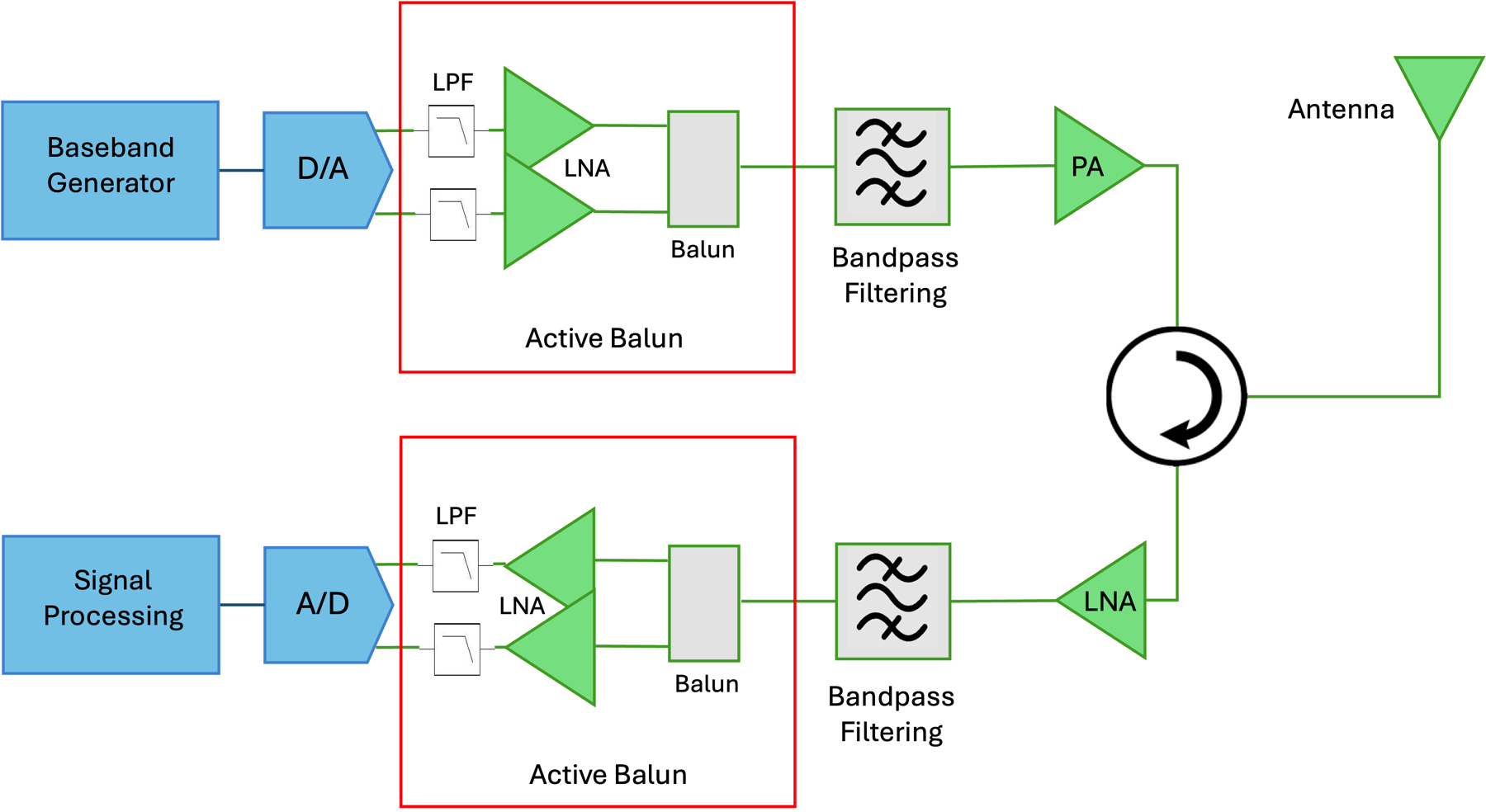
Active baluns bridge the microwave and digital worlds
To achieve the datasheet performance of ultra-high-speed data converters, now clocking to 64 GS/sec, the handoff to and from the microwave domain must be near perfect. To preserve the data converters’ spurious-free dynamic range, a new category of component has been developed that converts between the differential and single-ended signal domains while amplifying and filtering out-of-band signals.
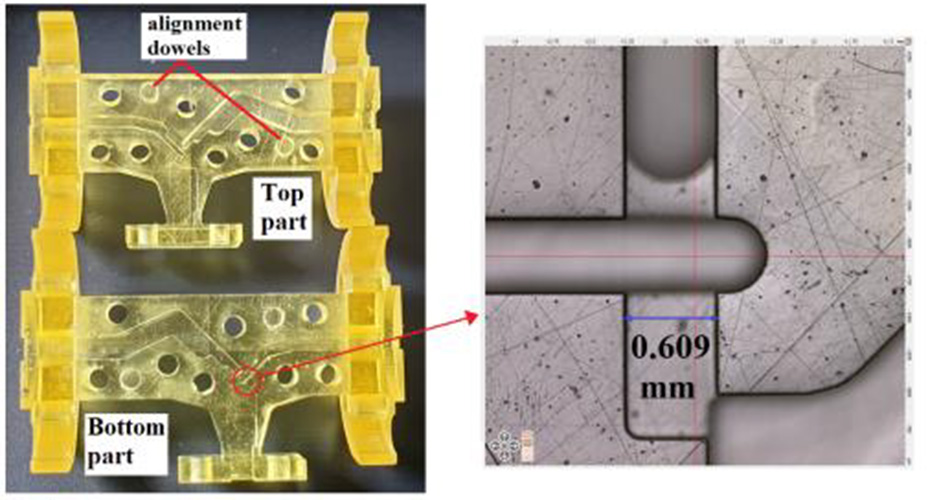
3D printing provides innovative approaches to GHz and THz components
High-precision stereolithography offers an innovative way to create active and passive components for the 100-GHz and even terahertz range.
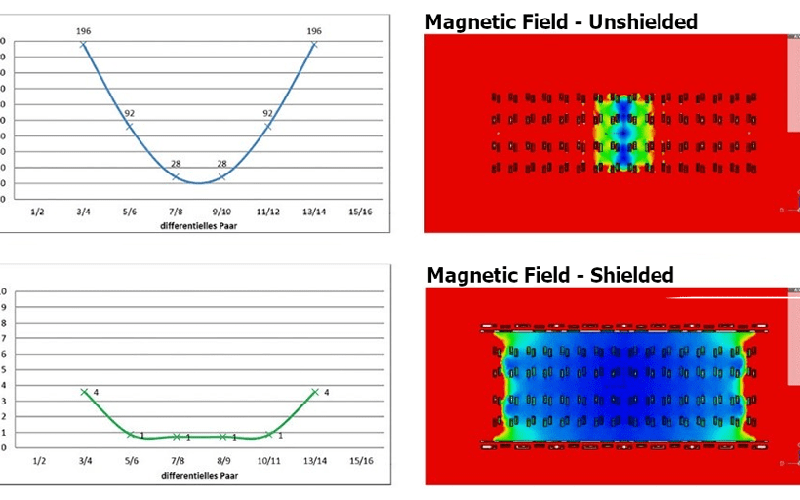
How does a 224 Gbps-PAM4 connector work?
Designing 224 Gigabits per second four-level pulse amplitude modulation (224 Gbps-PAM4) interconnects is challenging. But it’s required to support the demands of generative artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), 1.6 Terabits per second (Tbps) networking, and other high-speed applications in advanced data centers, as well as 5G and 6G communications infrastructure. At these elevated data…
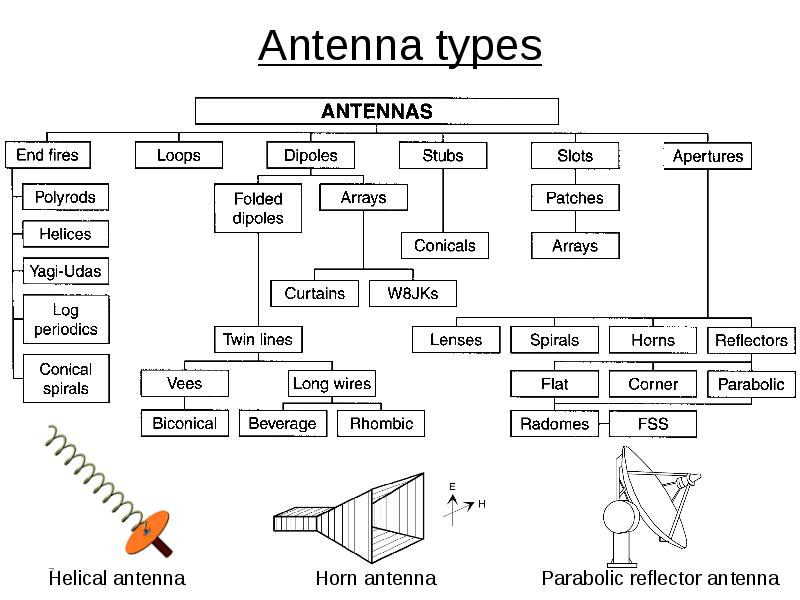
Ultra-wideband antennas meet unique spectrum needs
Ultra-wideband RF applications need specialized antennas to support their unusual spectrum and bandwidth characteristics. Ultra-wideband is a short-range, high-bandwidth wireless technology that offers precise positioning and tracking as well as highly secure communications. It can provide accurate distance measurements in real-time without interfering with conventional narrowband and carrier wave transmissions in the same frequency bands.…
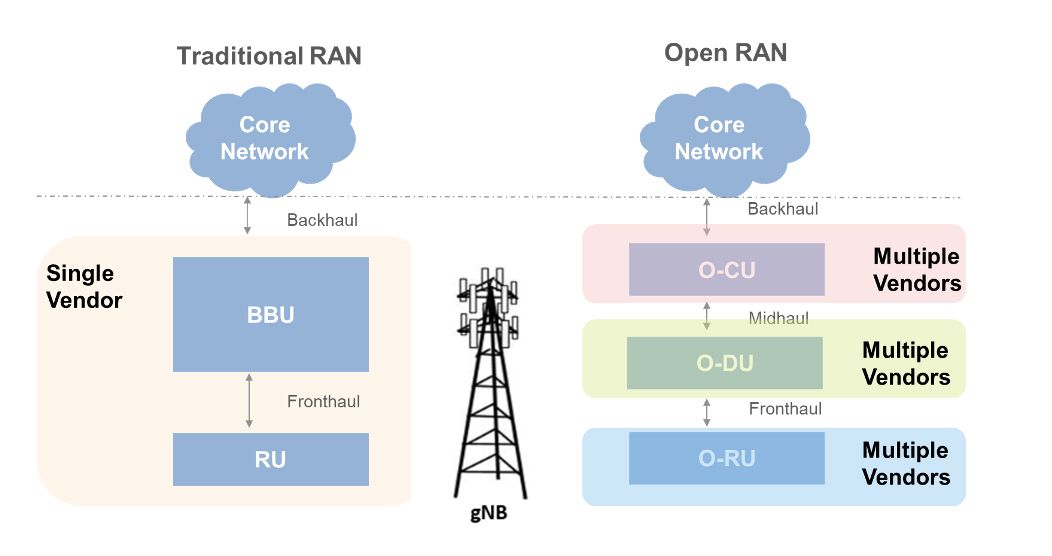
How do Open RAN interfaces work?
The O-RAN Alliance has developed specifications for communications interfaces between components of an Open RAN. This FAQ explains the functions of each.
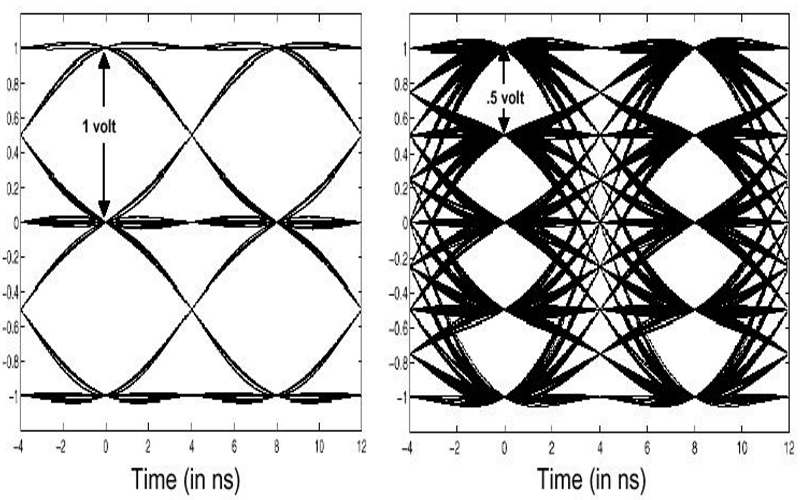
How does 4D-PAM5 work in Gigabit Ethernet?
Networks using 10 GbE rely on more sophisticated modulation and coding techniques than networks needed at lower data rates. 4D-PAM5 (four-dimensional five-level pulse amplitude modulation) are the encoding and modulation techniques used in Gigabit Ethernet (GbE). 4D-PAM5 replaced the multilevel transmit MLT-3 encoding and modulation used for 100BASE-TX. IEEE 1000BASE-T (GbE) uses a combination of…
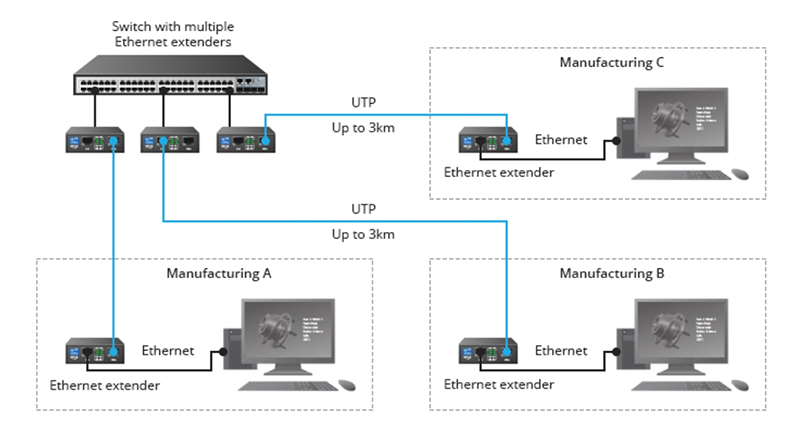
What’s the difference between an Ethernet extender and a media converter?
Extend the reach of Ethernet by converting the signals to different electrical or optical signals. Ethernet extenders and media converters can both be used to expand network coverage. Extenders operate over unshielded twisted pair (UTP) or coaxial cabling, while media converters change the signals from electrical to optical and back. Extenders and media converters can…
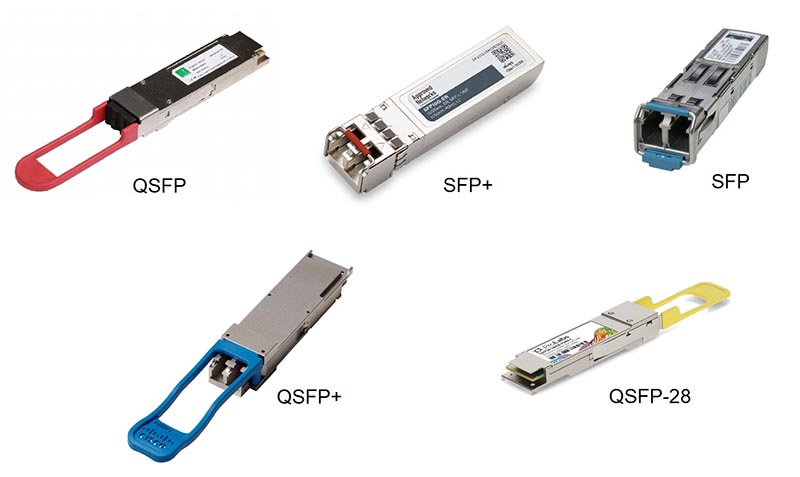
How do SFP, SFP+, and QSFP compare?
Pluggable modules come in many variants, each designed for a specific purpose. Small form factor pluggable (SPF) technology was developed to support high-speed interconnects between servers, storage, and communications equipment in data centers and similar environments. Over time, the multi-source agreement (MSA) that specifies SPF has evolved to include new formats, including SFP, SFP+, SFP28,…
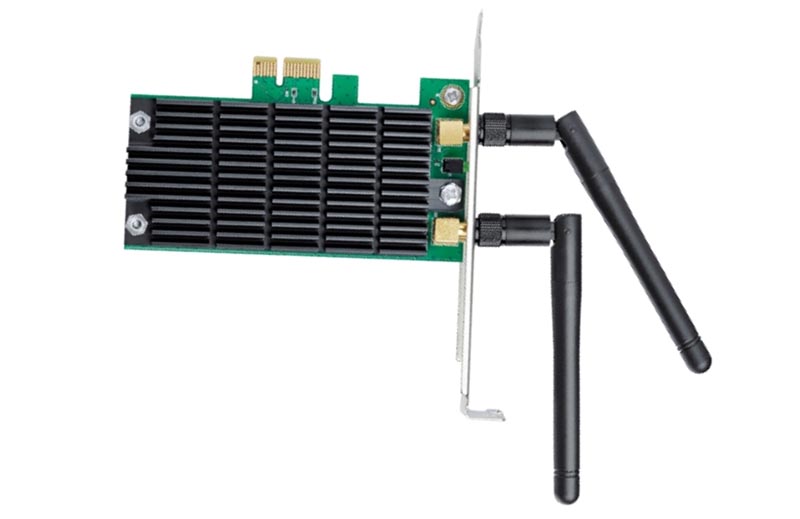
What’s a PCIe wireless adapter?
PCIe wireless adapters are one of the ways to connect a computer or server to a Wi-Fi network. There are different formats of PCIe wireless adapters, and there are also USB wireless adapters that compete with them based on convenience of operation. This FAQ reviews the operation of PCIe expansion cards, reviews the use of…